Fiber optics has revolutionized communications, providing unprecedented data transmission speeds and exceptional reliability. UFINET, with its vast experience, uses the key components of fiber optics to offer advanced solutions in the world of telecommunications.
Fiber optics, with its capabilities of transmitting data at astonishing speeds, has become the backbone of the modern communications infrastructure.
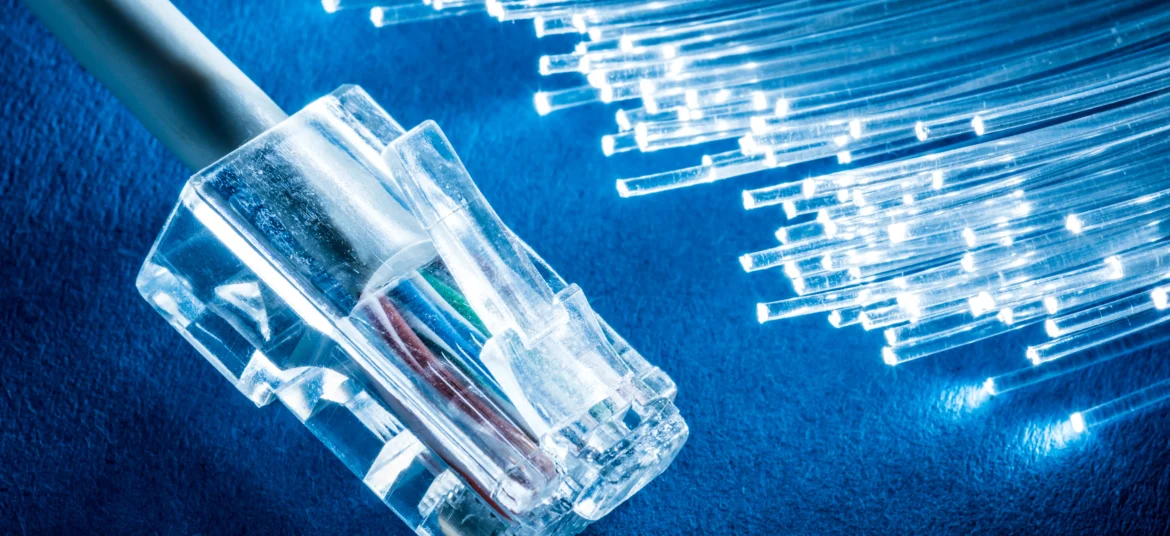
At the heart of the optical fiber is the core, usually made of glass or high purity plastic. This nucleus is the channel through which the light pulses that carry the information travel. Surrounding the core is the cladding, a layer with a lower refractive index that helps guide reflected light back to the core, thus facilitating light transmission along the fiber.
There are two main categories of optical fibers: single-mode and multimode. Multimode fibers have larger cores that allow simultaneous transmission of multiple light modes, while single-mode fibers, with thinner cores, support only one transmission mode.
An essential element for the protection and mechanical strength of the optical fiber is the buffer coating, a layer that surrounds the fiber and provides additional insulation. The outer jacket is the final protective layer that ensures fiber integrity in diverse environments.
The connection of optical fibers is done through connectors, which are used at the ends of the fibers to couple them with other devices or to splice them together. These connectors ensure efficient and lossless light transmission.
The individual components mentioned above are grouped into assemblies, forming what we know as fiber optic cable. These cables may contain single or multiple fibers, and their design may vary depending on whether they are intended for indoor or outdoor use.
In addition, transmitters and receivers are used to complete the fiber optic system. Transmitters convert electrical signals into pulses of light for transmission through the fiber, while receivers perform the reverse task, converting light into electrical signals at the receiving end.
Ingenious design and specialized components make fiber optics a vital technology in the construction of efficient, high-performance telecommunications networks. In addition, we will expand more potential over fiber optics:

Fiber optics: the invisible bridge to the cloud
Direct Cloud Connectivity: direct links to the cloud
Fiber optic technology emerges as the backbone driving direct connectivity to the cloud. Direct Cloud Connectivity, offered by vendors such as UFINET, redefines the way enterprises access and use cloud services, establishing direct links that maximize efficiency and minimize latency.
Fiber optics, a marvel of modern engineering, uses strands of glass or plastic to transmit data through pulses of light. This revolutionary technology has become the preferred medium for high-speed communications due to its ability to carry large amounts of data at astounding speeds and with minimal signal loss.
Key characteristics of optical fiber:
– Amazing speeds: Transmit data at the speed of light, literally.
– Giant bandwidth: Capacity to handle large volumes of data simultaneously.
– Low latency: Significant reduction in response time, vital for time-sensitive applications.
With companies’ increasing reliance on cloud services, access efficiency has become crucial. Direct Cloud Connectivity stands as an answer to this need, offering direct links to leading cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure and others.
Advantages of Direct Cloud Connectivity:
Minimum latency: By eliminating the public network, latency is reduced, guaranteeing minimum response times.
Increased security: By avoiding the public Internet, data travels over a private and secure connection.
Improved performance: The direct connection ensures more consistent and reliable performance.
Beyond public clouds
Direct Cloud Connectivity is not only limited to the most popular public clouds. UFINET, with its versatile approach, allows companies to connect to private clouds, expanding the options to suit the specific needs of each customer.
Connectivity Options:
Local connection: Simplifies connectivity to the public cloud and the Internet.
Remote connection: Accessible for seamless supplier changes.
Challenges overcome: fiber optics as an end-to-end solution
The path to direct cloud connectivity is not without its challenges, but fiber optics emerges as the end-to-end solution. Latency, security and performance issues are effectively addressed by implementing Direct Cloud Connectivity backed by a robust fiber-optic network. Additional benefits:
Scalability:Fiber optics allows unlimited scalability to meet growing data demands.
Stability: Ensures stable and reliable connectivity, essential for continuous business operations.
24×7 personalized attention: Through the Network Operations Center (NOC), UFINET offers personalized bilingual attention to guarantee continuous support.
The bright future of connectivity: fiber optics as a backbone
As businesses move towards an increasingly digital future, fiber optics is emerging as the pillar that underpins the evolution of connectivity. Direct Cloud Connectivity, powered by UFINET’s fiber-optic infrastructure, points to a horizon where speed, efficiency and reliability are unwavering imperatives.
Co-location: the invisible strategy for operational efficiency
Co-location, also known as collocation, emerges as a smart strategy for companies looking to optimize their operations. In the context of invisible nodes, co-location involves the installation of equipment from multiple clients in the same location, benefiting from shared facilities, security and advanced network connections.
Key benefits of co-location:
– Space efficiency: shared use of physical facilities to maximize space and reduce operating costs.
– Advanced security: facilities with robust security measures, from access control to fire prevention systems.
– Improved connectivity: access to a high-quality network infrastructure that facilitates fast and secure connections.
Data centers: the beating heart of digital connectivity
Data Centers are the epicenter of the digital revolution, housing the critical infrastructure that supports digital operations. Equipped with advanced servers, storage and networks, these data centers are essential to ensure the availability and performance of crucial online services.
Essential components of data centers:
High-performance servers
: powerful processing units that run applications and services.
Storage systems
Mass storage for data, files and applications.
Network infrastructure
advanced connectivity to ensure fast and secure data transmission.
Fiber optics in co-location and data centers: the invisible link
Fiber optics is the invisible link that connects and empowers both co-location and data centers. With its ability to transmit large amounts of data at unmatched speeds, fiber optics ensures fast and reliable connectivity between equipment housed in these strategic nodes. Crucial roles of fiber optics:
Internal connectivity
Fast connection between servers, storage and other equipment within data centers.
External links
High-speed connections between data centers and other facilities, allowing redundancy and scalability.
Challenges overcome: fiber optics as an end-to-end solution
Connectivity in the digital environment is not without its challenges, and this is where fiber optics presents itself as a comprehensive solution. Latency, signal loss and security issues are effectively addressed by implementing this technology in invisible nodes such as data centers and co-location facilities.
Additional advantages of fiber optics:
Infinite scalability:
Ability to handle increasing data demands without compromising performance.- Unwavering Reliability: Ensures stable connectivity, essential for continuous business operations.
Innovation enabler
Drives the adoption of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things.
The importance of connectors cannot be overlooked, facilitating the connection and splicing of fibers to build cohesive networks. The transition from electrical signals to light pulses, thanks to transmitters, and the reverse conversion in receivers, complete the transmission cycle, enabling fast and reliable communication.
In the current scenario, where the demand for bandwidth and transmission speed continues to increase, fiber optics stands out as the technology of choice. Its crucial role in connectivity, both in local area networks and long distance systems, sets a standard in communications efficiency. As digital infrastructure evolves, fiber optics will continue to play a pivotal role, powering global connectivity and paving the way for an interconnected, data-driven future.



