A Data Center, also known as a data center, is a physical infrastructure that organizations use to store, process, and manage a large amount of important data and applications. Due to the increasing digitization of information, these Data Centers have become an essential pillar for the operations of companies, government institutions and other entities that handle data at scale. One Data Center provides the environment needed to operate complex computing systems, manage a large amount of data, and manage networks that connect users to applications and services.
The Data Center It is a specialized facility specifically designed to house a variety of technology systems including servers, storage devices, networking, and security equipment. Its primary purpose is to ensure that business information and applications are available and secure at all times. The demand for these Data CenterS has grown exponentially with the rise of cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and e-commerce.
It should be known that a Data Center is characterized by several factors:
High availability:
Data centers are built to operate 24/7, ensuring that the services running there are always available.
Safety:
They include several layers of physical and digital security to protect the important data stored there.
Mass Storage Capacity:
They can manage and store large amounts of data in a variety of formats, including text files, entire databases, and media data.
Now, the history of Data Centerss begins with the growth of computing in the 1960s, when large companies began using mainframe computers. Because they are so expensive and bulky, businesses needed a dedicated, secure space to set them up. This marked the beginning of the first Data centers, which initially only existed for large organizations with enough money to invest in advanced technology.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, with the emergence of microcomputers and servers, the concept of Data Center Evolved. Businesses began to see the need for specialized facilities to host servers that provide business services such as email, databases, and financial applications. During this time, standards such as TIA-942 emerged that began to regulate the construction and operation of data centers, including factors such as redundancy, security, and environmental control.
With the rise of the Internet in the 2000s, the demand for data centerss increased significantly. Enterprises needed to handle large amounts of data globally, which led to the emergence of data colocation or commercial data centers, where organizations could rent space and resources in these specialized centers.
Today, cloud computing and virtualization have changed the data center landscape. Companies such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure have created massive, distributed data centers, where they offer cloud services globally, allowing businesses and users to access large amounts of computing resources without the need to build and maintain their own data center.
There are different types of Data Centers depending on the way they are used and managed:
- Enterprise data centers: are operated by specific organizations to manage and administer their own activities. These centers are generally within the company’s facilities and are only available for your use.
- Colocation data centers: They are operated by third parties and provide space, power, and connectivity to multiple customers. Businesses can take advantage of a company’s facilities and infrastructure. Data Center by renting space for your own servers.
- Cloud Data Centers: Cloud service providers, such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft, operate huge data centerss distributed all over the world. These centers allow companies to use storage and computing resources over the internet, without having to physically own or manage the servers.
- Data Centers Edge: With the growth of connected devices (IoT), smaller, distributed data centers have emerged close to end users to reduce latency in data processing. These Data centerss Edge are crucial for applications that require low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, real-time video streaming, and industrial data analytics.
A modern data center contains several key components that work together to provide data storage, processing, and connectivity:
- Servers: Servers are computers that process and store data. In a Data Center, servers are typically grouped into racks that can hold tens or hundreds of servers.
- Storage systems: Data is stored on specialized storage devices, such as hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs). The Data centers typically use storage networks, such as SANs (Storage Area Networks), to handle large volumes of data efficiently.
- Network infrastructure: Includes routers, switches, and firewalls that enable communication within the data center and between the data center and external users. The network also includes redundant connections to ensure that data traffic can continue to flow even if a connection fails.
- Cooling systems: Since servers and other electronic equipment generate heat, data centerss need advanced cooling systems to prevent equipment from overheating. HVAC systems control the temperature and humidity inside the facility.
- Power supply: Data Centerss require an uninterrupted power supply. This includes emergency power supplies, such as generators and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), to ensure that services continue to operate even during a power outage.
- Physical Security: Security in a Data Center it is critical. This includes access controls, camera surveillance, security guards, and authentication systems to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the facility.
Today, data centerss are the basis of the digital economy. Data centers are critical to the operation of all electronic transactions, cloud services, mobile apps, and social media. The expansion of data centers around the world has been driven by the growing demand for data storage and the need to process a large amount of data in real-time. . Today, data centers are the foundation of the digital economy. Data centers are critical to the operation of all electronic transactions, cloud services, mobile apps, and social media. The growing need for storage and processing of large amounts of information in real-time has driven the expansion of data centers around the world.
Businesses depend on data centerss to host your critical applications, ensure business continuity, and provide services to users around the world. As sectors such as e-commerce, banking, and telecommunications become more digital, data centers will continue to become increasingly crucial.
Technological advancements are strongly influencing the evolution of data centers. Some of the current and future trends include:
- Sustainability and energy efficiency: Since data centersIf they consume large amounts of energy, significant emphasis is being placed on reducing their environmental impact. Companies like Google and Microsoft are investing in Data centers with renewable energy and more efficient cooling technologies to reduce your carbon footprint.
- Virtualization and containers: These technologies allow multiple applications and operating systems to run on a single physical server, improving resource utilization and reducing the need for more hardware.
- Edge Computing: As the demand for real-time processing increases, data centerss Edge are gaining importance. These smaller data centers, close to end users, reduce latency and enable faster application execution.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to improve data center management, optimizing energy consumption, predicting failures, and improving security.
In conclusion, Data Centers It is an essential component of contemporary technological infrastructure. Business operations, innovation, and the digital economy depend on their ability to store, process, and distribute significant amounts of data. Data centers are crucial to ensuring the availability, security, and performance of the data that powers our digital lives, from large enterprises to cloud services.

What is a Data Center for?
A data center It is essential for the technological operations of a company, institution or organization to function properly, and its main function is to enable the secure and efficient management of large amounts of information. Data centers are not only important for data storage, but they also play an important role in providing vital services, supporting business applications, and facilitating connectivity over international networks.
The core purpose of a data center is to provide a controlled and secure environment where data can be processed, stored, and distributed effectively and reliably. Modern businesses rely heavily on the constant availability of and access to data and applications such as databases, business applications, e-commerce platforms, and financial systems.
Here are some of the main functions that Data Centersfulfill:
- Data Storage: Storing large amounts of data is one of the most notable functions of a data center. This includes information such as files, databases, backups, and any other type that is essential to the operation of an organization or company.
- Data Processing: Data centers not only store, but also process data. Servers in a data center run applications that perform computationally intensive operations, such as data analysis, financial calculations, and simulations.
- Distribution of services: Data centers provide services and applications to end users around the world. This includes real-time trading systems and web and mobile applications. One Data center must be able to deliver these services with low latency and high reliability for many businesses to succeed.
- Security and Backup: Data centers are designed to protect important data and applications. This includes multiple layers of physical and digital security, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. In addition, data centers often have backup and disaster recovery systems in place to make sure that information can be restored in the event of failures or catastrophic incidents.
- Scalability: One Data Center It allows organizations to scale their operations as they grow. As demand for a business or application increases, the Data Center can add more storage, compute, and network capacity to handle the increase in users and data without impacting performance or availability.
Data Centerss have a wide range of sectors that use them for a variety of purposes. Here are some examples of various industries that use data centers:
- Technology Companies: Companies like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft rely on huge data centers to provide cloud services, mobile apps, and operating systems to millions of people around the world. These data centers store data and run applications such as e-commerce platforms and search services.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and other financial institutions use Data Centers to manage financial transactions, store customer information, and secure their online payment systems. In a world where electronic transactions are the king of the market, data center infrastructure is crucial to ensure the integrity and security of these transactions.
- Governments: Governments use data centers to store large amounts of data related to citizens, such as health databases, tax records, and social security information. In addition, data centers provide the infrastructure needed to implement public management systems, allowing government agencies to operate efficiently.
- Health Sector: Data centers store important data about patients, medical histories, and treatment records in the healthcare industry. In addition, they support applications that allow doctors and hospitals to better manage patient care, improving coordination and precision in treatments.
- E-commerce: E-commerce sites like Amazon, eBay, or Alibaba rely on data centerss to process and store purchase transactions, customer data, and inventory records. These data centers must handle large volumes of traffic and transactions in real-time, ensuring that the platforms are available and secure for users.
Also the use of a Data Center It offers a number of advantages to organizations looking to store and manage large volumes of data efficiently. Here are some of the main benefits:
- High Availability: A Data Center It is designed to deliver a highly available environment, which means applications and data are available 24/7. This is particularly crucial for businesses that need continuous access to their systems and databases.
- Data Security: Data Centerss have strong security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. This includes both physical security and digital security, which includes access controls and surveillance, as well as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
- Cost Reduction: Many organizations choose to use daa centers or third-party cloud services to reduce their operational costs, even though building and maintaining a data center can be costly. Companies can significantly reduce hardware, maintenance, and energy expenses by outsourcing the management of their technology infrastructure.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The Data Centers allow businesses to expand their operations as they grow. As demand increases, organizations can increase their storage and processing capacity without making large upfront investments.
- Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: Data CentersModern systems are equipped with redundancy systems that ensure that data is protected against failures or disasters. This includes duplicating data across multiple locations and implementing disaster recovery plans that allow information to be restored in the event of failures.
The need for a Data Center It is driven by several factors, ranging from the increasing amount of data that companies generate and store, to the need to ensure the security and continuous availability of that data. In a world where technology powers business operations, Data centersprovide the critical infrastructure that enables businesses to be competitive and stay operational.
To conclude a Data Center It serves as the backbone of modern technology operations. Its ability to store, process, and distribute large amounts of data is crucial to the operation of a wide range of industries, from finance to e-commerce to healthcare. With the growing adoption of the cloud and the increasing importance of digital technology in the global economy, Data centerswill continue to play a key role in the future of business and technology.

How is a data center made?
The complex process of designing and building a data center It requires collaboration from various disciplines, from electrical engineering and architecture to computer science and security. One Data Center It should be designed to meet high standards of efficiency, security, and reliability while ensuring that the services it hosts are continuously available. Here are the essential steps for creating a data center, as well as important things to consider during planning, construction, and operation.
Data Center Planning
Planning is the first step in creating a data center. This process includes a thorough assessment of the organization’s needs, defining the project’s objectives, and selecting the right location. To ensure that the Data Center can meet the current and future needs of the organization.
Data Center Design
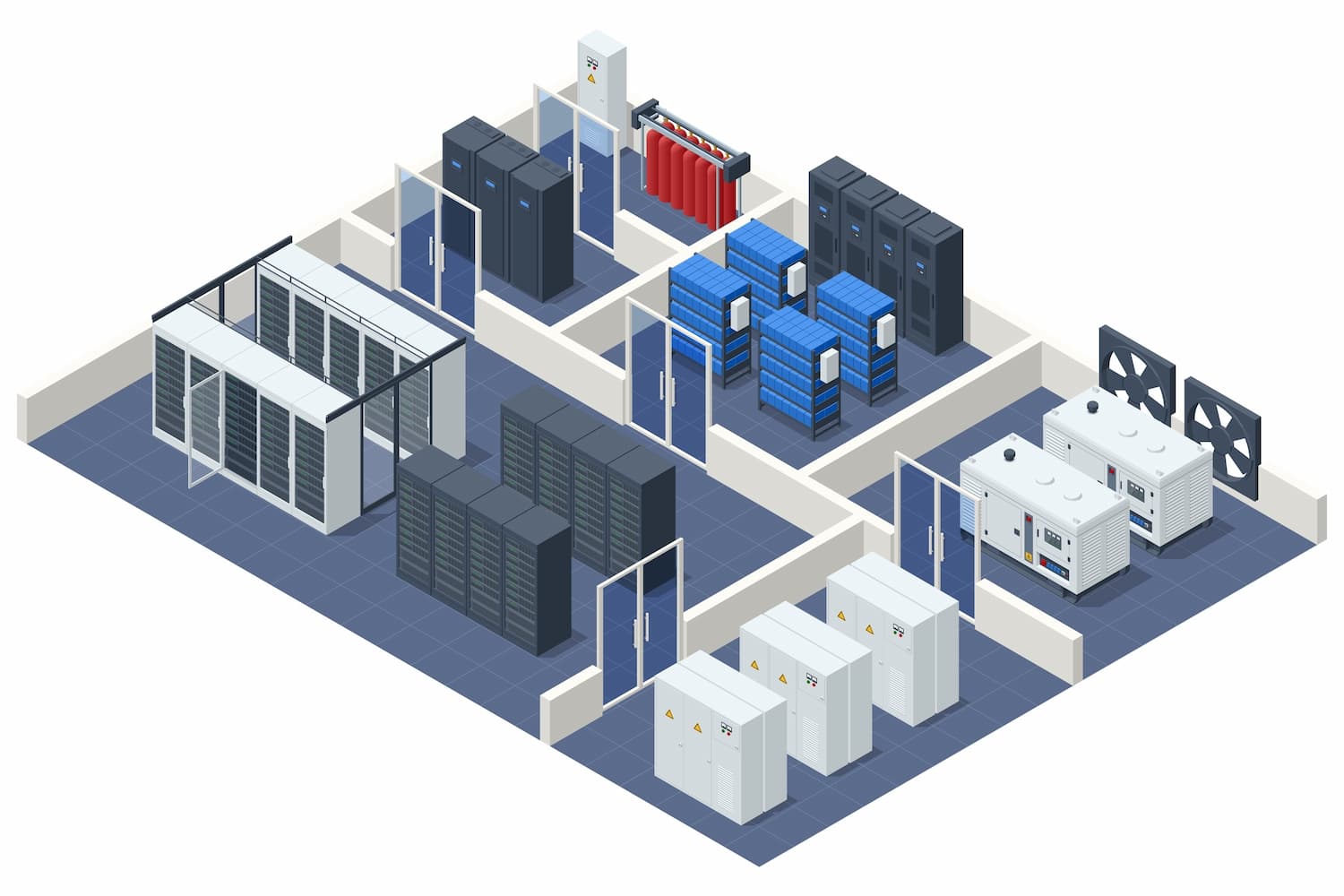
The design of a Data Center It requires the construction of an infrastructure that can meet the operational and technological needs of the company. This design must consider the physical arrangement of the components and the supporting infrastructure necessary to ensure their continued operation. Listed below are the essential elements of a data center design.
- Physical Space Design: The Space Within a Data Center It must be carefully designed to house servers, storage, and network components. Racks and cabinets should be placed to maximize airflow and ease of maintenance. Network infrastructure, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and refrigeration equipment should be located in separate areas.
- Energy Systems: A Data Center It consumes large amounts of energy, and the stability of the electricity supply is critical to its operation. The design should include redundant power systems, such as backup generators and UPS systems, to ensure that equipment continues to operate even in the event of a power outage. In addition, it is essential to implement an efficient power distribution system to minimize energy waste.
- Cooling systems: Data center equipment They produce a significant amount of heat, which can have a negative impact on their operation if not handled properly. It is essential to design HVAC and refrigeration systems to maintain temperatures at the appropriate intervals. Cooling systems should be positioned in a way that allows for efficient airflow and avoids hot spots that can damage servers.
- Network Infrastructure: A Data Center it must be connected to multiple Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to ensure redundancy and fast access to the global network. Network infrastructure design should include switches, routers, and firewalls that secure internal and external data traffic efficiently and securely. Redundant network connections are key to ensuring that services are always available, even in the event of a failure in one of the connections.
- Physical Security: A Data Center It must be designed to withstand physical threats such as theft, vandalism, or entry. This implies, depending on the sensitivity of the data being handled, installing access control systems, security cameras, biometric authentication systems and security guards. In addition, the use of smoke detection and fire suppression systems that do not damage electronic equipment is crucial.
Data Center Construction
Once the design has been completed, the physical construction of the Data Center begins. This phase includes the construction of the structure, the installation of the electrical and air conditioning systems, and the integration of the computer and network equipment. The construction of a Data Center must be run according to strict quality and security standards to ensure that the infrastructure meets operational expectations.
- Construction of the Structure: The first phase of construction involves the creation of the building or physical structure where the Data Center will be located. In addition, it is important to consider waterproofing and dust control to keep the environment clean and safe for electronic equipment.
- Electrical Infrastructure Installation: One of the most critical parts of building a Data Center is the installation of the electrical infrastructure. This includes laying cables, installing backup generators and UPS systems, and integrating electrical panels that will distribute power to the different components.
- Installation of Refrigeration Equipment: HVAC systems are installed during this phase to ensure that the data center is not in the right place. maintain a stable temperature. This can include precision air conditioning systems, as well as water chillers or air cooling systems.
- Assembly of Computer and Network Equipment: Once the structure and support systems are in place, the computer and network equipment is installed. This includes rack placement, server installation, storage devices, and network switches. During this phase, technicians also connect systems to internal and external networks, and configure devices for operation.
Testing and Validation
After completing the construction of the data center and the installation of all equipment, it is essential to perform extensive tests to ensure that the entire system is working properly. Validation of power systems, network infrastructure, cooling systems, and safety measures are all part of these tests. In addition, failure simulations should be carried out to verify that redundancy measures are working as expected.
- Energy Testing: Tests are performed to make sure that the primary and backup power systems are working properly. This includes power outage simulations to validate that UPS systems and generators are automatically activated and that the Data Center continues to operate without interruption.
- Network Testing: Network systems must be tested to ensure that both internal and external connectivity is working properly. This involves validating network redundancy, as well as speed and latency testing to ensure optimal performance.
- HVAC Testing: Refrigeration systems must also be tested to ensure they can handle the thermal loads of the data center. During these tests, different operating scenarios are simulated to check that temperature and humidity are kept within the recommended ranges.
- Safety Testing: Physical security systems, including access controls and surveillance cameras, are tested. In addition, fire protection systems and security alarms are tested to ensure that they function properly in the event of an emergency.
Data Center Operation and Maintenance
To ensure data center performance In the long term, continuous operation and maintenance are essential. The operation of a Data center includes monitoring critical systems, tracking environmental conditions, and managing services running in the data center.
- Systems Monitoring: A Data Center it must be monitored in real time to detect possible problems before they affect its operation. This includes monitoring the grid, power systems, and temperature levels. Data center infrastructure management (DCIM) tools allow administrators to centrally monitor these systems and receive alerts when problems arise.
- Preventive Maintenance: To avoid unforeseen failures in the data center, regular preventative maintenance is essential. This includes inspecting and cleaning equipment, checking power systems, and updating applications and software running on servers.
- Equipment Upgrade: As systems age or technological demands change, data center equipment may need to be upgraded or replaced . This should be done in a planned manner to avoid interruptions in services.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: A Data Center You should have a disaster recovery plan in place to ensure that data and applications can be restored quickly in the event of a failure or catastrophic event. This may include replicating data in secondary data centers or deploying cloud recovery solutions.
Building a Data Center It’s a methodical process that requires constant planning, design, construction, testing, and maintenance. One Data Center A well-designed and operated system ensures the availability and security of vital data and services, enabling organizations to operate efficiently and without interruption. The Data centerswill continue to play a crucial role in supporting global digital infrastructure as technology continues to evolve.

What is stored in a data center?
Many modern organizations rely on data centerss, where important applications are centralized, secured, and executed. The Data Center It not only stores data, but also processes, analyzes, and makes it accessible to various systems and users worldwide. It is critical to understand what is stored in a data center to determine its importance and its role in the digital world.
Types of Information Stored in a Data Center
- Systems Monitoring: A Data Center it must be monitored in real time to detect possible problems before they affect its operation. This includes monitoring the grid, power systems, and temperature levels. Data center infrastructure management (DCIM) tools allow administrators to centrally monitor these systems and receive alerts when problems arise.
- Preventive Maintenance: To avoid unforeseen failures in the data center, regular preventative maintenance is essential. This includes inspecting and cleaning equipment, checking power systems, and updating applications and software running on servers.
- Equipment Upgrade: As systems age or technological demands change, data center equipment may need to be upgraded or replaced . This should be done in a planned manner to avoid interruptions in services.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: A Data Center You should have a disaster recovery plan in place to ensure that data and applications can be restored quickly in the event of a failure or catastrophic event. This may include replicating data in secondary data centers or deploying cloud recovery solutions.
Corporate and Business Data:
A data center It has one main function which is to store the crucial data of a company or business. Financial records, customer records, inventory databases, and employee records are some of these data. The Data centersprovide secure infrastructure to protect this sensitive information from unauthorized access or loss as a result of system failures.
-
- Financial Records: Financial statements, invoices, payments, and other accounting-related documents are stored and processed in the Data Centers. This type of information is vital for any company, as its correct management is key to business decision-making. Financial systems need fast, secure accessibility to execute transactions and generate reports.
- Customer Databases: Customer Databases: The Data Center It manages all customer information, including names, addresses, emails, and transactions. Businesses rely on this information to provide customer support, create marketing campaigns, and provide personalized services. Due to the sensitive nature of this data, robust security measures must be implemented to protect it from attacks or data theft.
Application and Software Data:
Data centersThey also store applications and software in addition to static information. The Data Centers host numerous business applications, including customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and e-commerce platforms. This includes internal applications and services for external customers, such as software as a service (SaaS).
-
- Business Applications: Businesses of all sizes depend on critical business applications, which can range from accounting systems to HR applications. These apps store your data on the Data Centers, ensuring that they are always available for use and operation without interruption.
- Operating Systems and Management Software: Server operating systems, as well as software that manages storage, networking, and security services, also reside within the Data Center. These systems must be kept up-to-date and secure to ensure efficient and secure operation of the data center.
Media Files
Many companies and digital platforms store media files in the Data CenterThese include photos, videos, audio, and other multimedia formats. Platforms such as YouTube, Netflix, or even cloud storage systems such as Google Drive or Dropbox, depend on the Data Centers to save and distribute these files to millions of users around the world.
-
- Videos and Streaming: The Data Centers are used by video platforms and online streaming services to store and distribute large libraries of content. Data centers ensure that media files are available with low latency and high quality, as fast access and efficient video delivery are crucial to the user experience.
- Photographs and Graphics: Platforms that allow users to store and share images, such as social media or cloud storage services, rely heavily on Data Centers. These files take up a considerable amount of space, so it’s critical that data centers offer scalable capacity and sufficient capacity to handle millions of images.
Cloud Databases
Many companies and individuals choose to store their data in cloud storage services, which are managed through Data Centers distributed all over the world. These services allow users to access their files from anywhere and at any time. Companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud manage gigantic Data centers that facilitate the storage and processing of data in the cloud.
-
- Relational databases: Many business applications use relational databases, which are stored in data centerss. Businesses can organize and retrieve data in a structured way with these databases, which use query languages such as SQL.
- NoSQL Storage: The popularity of web and mobile applications has driven the use of NoSQL databases. The Data centersmanage these databases, which store large amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data, such as social media messages and information from IoT devices.
Backup and Disaster Recovery Data
A data center It also serves as a backup storage center. Companies frequently use Data Centers to keep backups of your important data, ensuring that information is available in the event of a failure in the main systems. Backup is essential in disaster recovery plans because it allows normal operation to be restored in the event of an accident.
-
- Server and Application Backups: Critical servers and applications are regularly backed up to data centersto ensure that, in the event of a system failure, data can be recovered quickly without interruption to business operations.
- Disaster Recovery: In the event of a catastrophic event, such as a fire, earthquake or cyberattack, data centerss offer recovery solutions that allow systems to be restored quickly and efficiently. Data can be duplicated and stored in secondary data centers, located in different geographic regions, ensuring business continuity.
Big Data and Analytics
Data centers They are essential for storing and processing the large volumes of unstructured data generated by modern applications. This includes data collected from Internet of Things sensors, social media, e-commerce transactions, and other systems that generate big data. This data is used for real-time analytics, business intelligence, and data-driven decision-making.
-
- Internet of Things (IoT) Data: As more devices are connected to the internet, a massive amount of data is generated that needs to be stored and processed. The Data centersstore this information, which can be used for industrial applications, smart cities, or to monitor and analyze user behavior patterns.
- Analytics and Data Science: Companies that perform analysis of large data sets store this data in the Data Centers. The processing and storage capacity of a Data Center is essential to perform advanced analyses, which allow identifying trends and patterns that improve decision-making in the organization.
Security Logs and Monitoring
- A Data Center It also stores records of security-related events, both of networks and computer systems. These logs are crucial for monitoring potential security incidents, conducting audits, and detecting anomalous behavior that may pose threats to the organization.
- Computer Security Records: They include data about unauthorized access attempts, authentication failures, and changes made to systems. These records are stored in Data centersand can be reviewed by security teams to identify potential cyberattacks.
- Performance Monitoring Logs: Data CentersThey also store data on the performance of the systems, which are used to optimize the operation of the applications and prevent possible failures. These logs include information about CPU, memory, and network bandwidth usage.
Data storage in a data center It goes beyond simply saving information. The Data CenterS are complex infrastructures designed to handle large volumes of data securely, efficiently, and reliably. From corporate data to media files and security logs, the Data Center is the core that supports the digital operation of any organization in the modern world.



